Eurozone Inflation Slightly Rises to 2.6% in July 2024
20.08.2024 16:00 1 min. read Alexander Stefanov
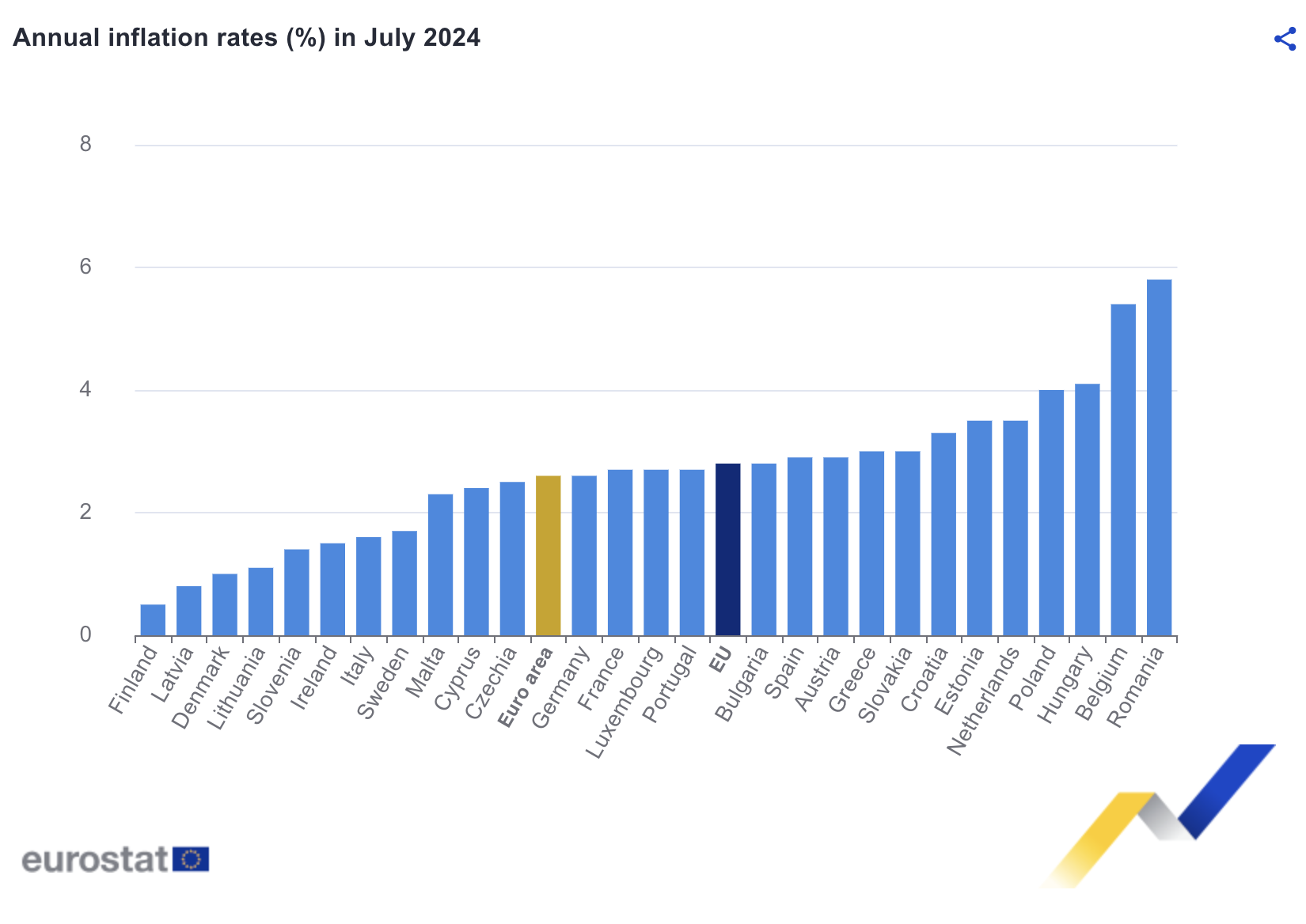
In July 2024, inflation in the eurozone increased slightly to 2.6%, up from 2.5% in June.
This is a decrease from the 5.3% rate recorded in July of the previous year. Meanwhile, inflation across the European Union rose to 2.8% in July 2024, compared to 2.6% the previous month, and down from 6.1% a year ago.
These statistics are provided by Eurostat, the European Union’s statistical office.
The lowest annual inflation rates were seen in Finland (0.5%), Latvia (0.8%), and Denmark (1.0%). Conversely, Romania (5.8%), Belgium (5.4%), and Hungary (4.1%) reported the highest rates.
Between June and July 2024, nine EU countries experienced a decrease in annual inflation, four saw it remain unchanged, and fourteen observed an increase.
In July, services had the largest impact on the euro area’s annual inflation rate, contributing +1.82 percentage points, followed by food, alcohol, and tobacco (+0.45 pp), non-energy industrial goods (+0.19 pp), and energy (+0.12 pp).
-
1
Trump Targets Powell as Fed Holds Rates: Who Could Replace Him?
27.06.2025 9:00 2 min. read -
2
U.S. PCE Inflation Rises for First Time Since February, Fed Rate Cut Likely Delayed
27.06.2025 18:00 1 min. read -
3
Key U.S. Economic Events to Watch Next Week
06.07.2025 19:00 2 min. read -
4
Gold Beats U.S. Stock Market Over 25 Years, Even With Dividends Included
13.07.2025 15:00 1 min. read -
5
U.S. Announces Sweeping New Tariffs on 30+ Countries
12.07.2025 16:30 2 min. read
US Inflation Heats Up in June, Fueling Uncertainty Around Fed Cuts
U.S. inflation accelerated in June, dealing a potential setback to expectations of imminent Federal Reserve rate cuts.
Gold Beats U.S. Stock Market Over 25 Years, Even With Dividends Included
In a surprising long-term performance shift, gold has officially outpaced the U.S. stock market over the past 25 years—dividends included.
U.S. Announces Sweeping New Tariffs on 30+ Countries
The United States has rolled out a broad set of new import tariffs this week, targeting over 30 countries and economic blocs in a sharp escalation of its trade protection measures, according to list from WatcherGuru.
Key U.S. Economic Events to Watch Next Week
After a week of record-setting gains in U.S. markets, investors are shifting focus to a quieter yet crucial stretch of macroeconomic developments.
-
1
Trump Targets Powell as Fed Holds Rates: Who Could Replace Him?
27.06.2025 9:00 2 min. read -
2
U.S. PCE Inflation Rises for First Time Since February, Fed Rate Cut Likely Delayed
27.06.2025 18:00 1 min. read -
3
Key U.S. Economic Events to Watch Next Week
06.07.2025 19:00 2 min. read -
4
Gold Beats U.S. Stock Market Over 25 Years, Even With Dividends Included
13.07.2025 15:00 1 min. read -
5
U.S. Announces Sweeping New Tariffs on 30+ Countries
12.07.2025 16:30 2 min. read